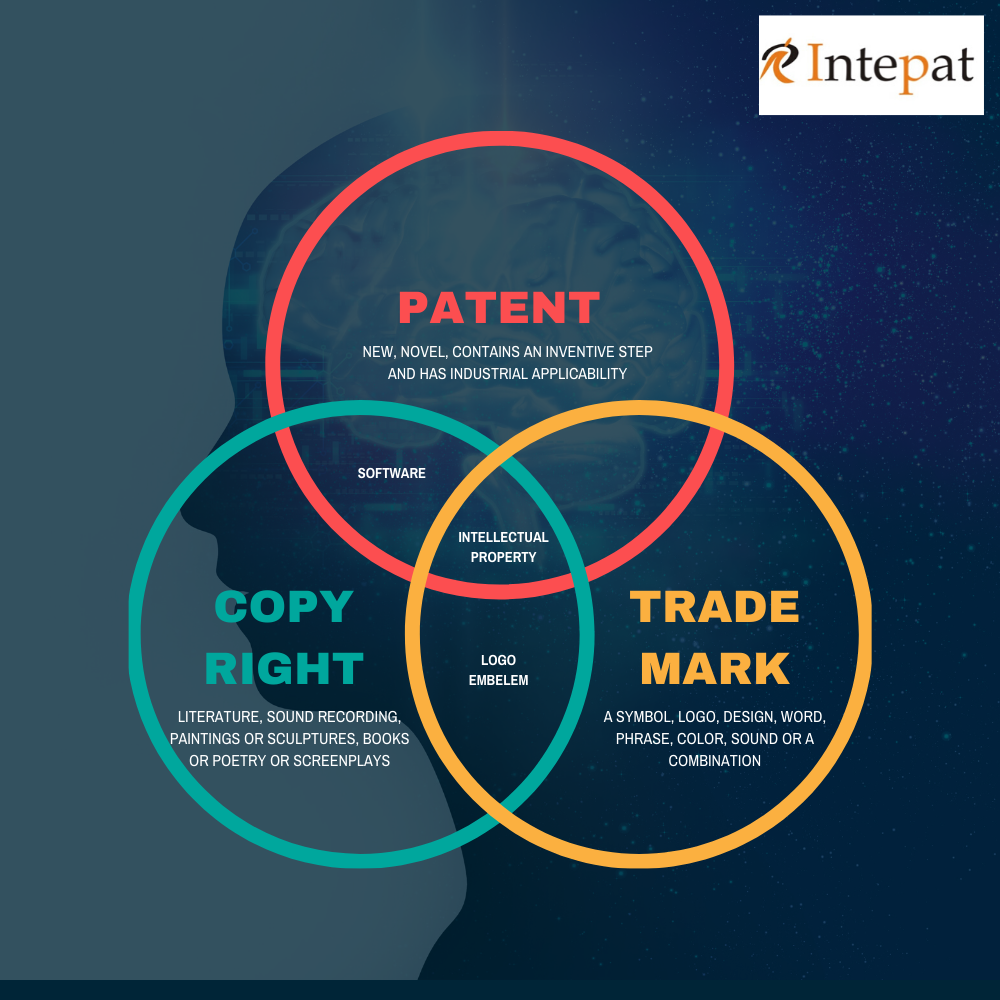
Copyright Vs. Trademarks Vs. Patents
The protection of Intellectual property often goes unnoticed by business owners. Very few business or startup owners understand the importance of safeguarding their Intellectual Property in the long run. Therefore, it is vital for a business owner, a startup owner, a creative person, or an inventor to have clarity about the concepts of Trademarks, Copyright, and patents.
1. Copyright
Copyright is also a tool to protect intellectual property, which can be in the form of literature, sound recording, paintings or sculptures, books or poetry or screenplays, etc. It grants the exclusive right to the creator of the work to specifically copy or reproduce or publish the work for monetary gains or otherwise. It doesn’t specifically require registration of the copyright.
Economic Rights:
Apart from this, the Copyright Act also provides the Proprietor with an economic right to reproduce the work, issue copies, perform or communicate it to the public, make any cinematograph film or sound recording, or make any adaptation or translation of the work.
Section 14 of the Copyrights Act provides for economic rights. Economic rights are rights that aid the author of the work in reaping economic benefits. This section highlights the importance of the exclusive right that the author provides to do or authorize the acts provided under the Act.
Paternity Rights
In addition, the Copyrights Act provides a paternity right which means the right to claim authorship of the work; an integrity right- the right to protect one’s honor and reputation and a general right- the right to not have a work falsely attributed to oneself. These moral rights remain with the author even after the copyright assignment.
The Copyright Registration:
Registration of copyright provides the creator of the artistic, dramatic, or musical work the exclusive rights to use and distribute their creation by prohibiting anyone other than the creator from reproducing or selling the copyrighted work online or offline.
Validity of Copyright:
1. Individual and Non-Individual Owner:
For an individual owner, the term of copyright is the author’s lifetime plus 60 years, whereas, for a non-individual owner, the copyright may last up to 60 years from the publication date.
b. Cinematograph
Further, for cinematograph films, sound recordings, photographs, posthumous publications, anonymous and pseudonymous publications, works of government, and works of international organizations, Copyright protection subsists for a period of 60 years from the year of publication. In the case of unpublished Cinematograph films, Photographs, and computer programs, the copyright subsists for up to 60 years from the year in which the original work was created.
c. Sound Recording
Further, the Copyright for Sound recordings is valid for 60 years from the end of the year when that sound recording is published for the first time. Broadcast reproduction rights are valid for 25 years from the year of broadcast, and performers’ rights last for 50 years from the year the performance was made.
Benefits of Copyright Registration:
The symbol © is used to protect copyrighted original works. It doesn’t mandatorily require registration, but registration proves originality. Copyright registration is necessary if you anticipate contravention. Copyrights are valid for the lifetime of the author plus 60 years. The copyright registration fee varies according to work in question.
Additional Advantages:
a) Legal Framework – At a bare perusal, it can be noted that Copyright grants legal protection to the Proprietor. Once the registration is completed, it gives legal shelter to the proprietor.
b) Prevention of financial loss – One of the assured advantages of copyright protection is limiting losses arising from duplicating copyrighted work.
c) Notifying the public about the ownership – Ownership is constantly at stake in issues on Copyrights. Copyright registration creates a public record of copyright ownership and helps establish the ownership of the Proprietor.
Trademark
A trademark is a symbol, logo, design, word, phrase, color, sound, or a combination of these used to trade goods or provide services. It indicates the source of goods and services and distinguishes them from the goods and services of others. It gives the exclusive rights to use a trademark concerning the product or service.
Industrialization and the growth of the system of the market-oriented economy allow competing manufacturers and traders to offer consumers a variety of goods in the same category.
Trademark is important because consumers need to be given guidance that will allow them to consider the alternatives and choose between the competing goods. For instance, without a logo, consumers may be unable to differentiate between Thumbs Up and Coca-Cola.
Scope of Trademark Protection:
Indian trademarks are divided into 45 classes. Classes 1 to 34 are for goods, and classes 35 to 45 are for services. This categorization forms a hierarchy of which trademark belongs to which category.
Trademark proprietors must make a registration application for each to register the name, logo, or slogan.
A trademark owner can be an individual, business organization, or legal entity. The trademark registration is valid for ten years, which the trademark owner can renew further.
Benefits of Trademark registration:
1. Registration of a trademark provides legal proof and public notice of the ownership. Registered trademarks use the ® symbol.
2. A registered trademark retains the exclusivity of the associated goods or services in the market and prevents other competitors from using similar kinds of marks or texts in their branding.
3. Trademark registration is for the brand establishment and trust in customers’ minds.
Patent
A patent is an exclusive right given to the inventor. Such a patent is a legal document granted when the invention is novel, inventive, and has industrial applicability. Further, a patent granted for an invention gives the right for a limited time to stop others from making, using or selling the invention without permission from the patent owner. Moreover, a patent can also be licensed, mortgaged, bought, or sold.
The scope of Patents:
Patents are territorial rights given to the patentee. Therefore, an Indian patent will give the patent owners the right in India to exclude others. The patent owner can even stop others from importing products into Indian territory if the patent owners hold an Indian patent. The Patent Act 1970 governs patent filing and prosecution in India, and The Patent Rules 2003.
The patent application can be made alone or jointly by the inventor, assignee, or legal representative of the deceased inventor or assignee.
The rights granted to a patentee are highlighted within Section 48 of The Patent Act 1970. The Section provides a patentee has exclusive rights to use, sell, exercise, or distribute the patented article. It is further important to highlight that the patentee’s rights subsist only during the term of the patent.
Benefits of Patent:
The patent is granted for 20 years from the date of application, for which the patentee must pay renewal fees yearly. If the fee is not paid within the stipulated time, the rights will cease to exist. A patent protects an invention for 20 years but cannot be renewed beyond that.
A provisional patent lasts for a year. The fee to be paid with the patent application is INR 1600/- for an individual applicant.
It has to be understood that a patent doesn’t give a right to make, use, or sell an invention. In contrast, a patent is a right to exclude others from making, using, selling, or importing the patented invention during the patent term.
Differences between Copyrights, Trademarks, and Patents:
| CRITERIA | COPYRIGHTS | TRADEMARKS | PATENTS |
| Governing Law | The Copyright Act, 1957 | The Trademarks Act, 1999 | The Patents Act, 1970 |
| Kind of protection within its ambit | Copyrights Act protects original creative expressions, which inclusive of literary works, artistic works, dramatic works, cinematography, etc., | The Trademarks Act protects a brand name that consists of either name, slogan, logo, shape, color, etc., for example, the unique color purple of Cadburys. | The Patents Act protects inventions that are novel, original, and distinct and that have an industrial value. |
| Validity | Valid for the author’s lifetime + 60 years after his/her death. | Validity for ten years can be made perpetual by renewing the trademark every ten years. | Validity for 20 years starting from the day the application is first made. It is also a territorial right, and therefore it is effective only within the territory of India. Separate patents must be filed for each country where protection is required. |
| Provisional Application Requirement | For a Copyright, there requires no provisional application. | A Trademark requires no provisional application; however, a trademark search is needed. | In Patents, a provisional application can get a person 12 months to file a complete specification and claim the priority date. |
| Renewal | Copyrights that are created after January 1st, 1978, cannot be renewed after the term has elapsed. | Trademarks can be renewed after a period of 10 years. | The Patent Renewal is required for 20 year validity period, and the Patent cannot be renewed after 20 years. |
| BENEFITS | Copyright registration provides the creator with the exclusive right to the work’s creator to copy, reproduce or publish the work for monetary gains or otherwise. | Registration of a Trademark ensures that the Brand name is protected and provides legal proof of ownership. | A patented Invention is tradable; the Patentee has the right to sell his patent if he feels that the patent can be commercialized. |
[cherry_button text=”Have Questions? Reach Us” url=”https://www.intepat.com/contact-us/” style=”info” centered=”yes” fluid_position=”right” icon_position=”top” bg_color=”#ea9525″ min_width=”33″ target=”_blank”][cherry_button text=”CONNECT WITH EXPERTS TO GET YOU FTO SEARCH” url=”https://www.intepat.com/contact-us/” centered=”yes” fluid_position=”right” icon_position=”top” bg_color=”#1e73be” min_width=”33″ target=”_blank”][/cherry_button]