In today’s intellectual property (IP) ecosystems, significant challenges persist in managing, protecting, and leveraging IP assets effectively. Among the major issues in IP business operations are the time-intensive and costly processes involved in managing IP, exacerbated by uncertainty in data accuracy and competition distrust. Moreover, the reliance on multiple, often incomplete data sources further complicates matters. However, blockchain technology presents a compelling solution by offering a single version of “the truth” regarding IP assets. By leveraging blockchain, organizations can increase the accuracy, efficiency, verifiability, transparency, and public access to information related to IP assets. Through immutable record-keeping and smart contracts, blockchain provides a secure and transparent platform for managing IP rights, facilitating collaboration, reducing disputes, and unlocking new opportunities for innovation and monetization.
WIPO: Blockchain and IP Ecosystem
The Blockchain Task Force was formed by the member states of the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO) under the direction of the Committee on WIPO Standards (CWS), with the objectives specified in CWS Task No. 59. Following its mandate, the Blockchain Task Force is developing a new WIPO standard to facilitate the possible integration of blockchain technology into intellectual property ecosystems by tackling issues related to governance, legislation, and interoperability.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has been at the forefront of organising events that explore the intersection of blockchain technology and intellectual property (IP) rights.In recent years, WIPO has organised several notable events focused on blockchain and its potential applications in the realm of intellectual property. One such event is the “Blockchain Whitepaper for IP Ecosystems,” held in 2021. This event provided an opportunity for experts and stakeholders to delve into the intricacies of blockchain technology and its relevance to the management and protection of IP rights. Before this, WIPO conducted a webinar in 2020 specifically dedicated to discussing the findings and insights outlined in the “Blockchain Whitepaper” and organised a Standards Workshop on Blockchain in 2019.
The intersection of Blockchain and IP: The Key Attributes
Blockchain technology and intellectual property (IP) have a fascinating relationship since blockchain provides creative answers to many of the problems related to the preservation, administration, and enforcement of IP rights.
Fundamentally, the capacity of blockchain technology to generate an immutable and transparent ledger makes it especially useful for documenting the production, ownership, and transfer of intellectual property rights. This feature refers to the capability of blockchain technology to allow artists (or any creators) to establish a clear and immutable record of when their creations were made. By timestamping their work on a blockchain, creators can create a tamper-proof record that shows undeniable evidence of their ownership of the copyright associated with that creation.
Moreover, blockchain facilitates more effective digital rights management (DRM) through the use of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automate content distribution, licencing agreements, royalty payments, and other IP management tasks. Smart contracts lower the danger of piracy and increase transparency by directly encoding terms into code.
Blockchain technology is based on decentralisation, which does away with the necessity for centralised agencies to administer and enforce intellectual property rights. Because it is decentralised, there is less chance of censorship or manipulation amongst the parties participating in intellectual property transactions.
Blockchain also makes it possible to tokenise intellectual property assets, turning ownership or usage rights into digital tokens. By trading these tokens on blockchain-based markets, authors can directly and independently monetise their intellectual property.
Potential Applications in IP Ecosystems
Blockchain technology offers a wide array of potential applications across both horizontal and vertical domains within intellectual property (IP) ecosystems. Horizontally, blockchain can serve as a foundation for digital identity management, fostering trust in data sharing among stakeholders. Its timestamping capabilities provide a robust mechanism for establishing the existence of intellectual assets, while provenance authentication ensures the integrity of asset ownership records. Beyond these, blockchain holds promise for numerous other horizontal uses, each leveraging its decentralized and immutable nature to enhance efficiency and transparency.
Vertically, blockchain applications are tailored to the specific needs of IP management. It can revolutionise IP registers by providing a secure and transparent platform for recording and verifying IP rights. Additionally, blockchain facilitates evidence of trademark use, offering a tamper-proof method for documenting the use of trademarks in commerce. The technology streamlines the transfer and licensing of IP rights, ensuring secure and verifiable transactions. Furthermore, blockchain enables precise management of IP ownership, simplifying complex ownership structures and reducing disputes. Finally, blockchain-powered priority document exchanges enhance the efficiency of IP processes, accelerating innovation and enforcement efforts. In essence, blockchain’s potential applications in IP ecosystems span a broad spectrum, promising to reshape how intellectual property is managed, protected, and leveraged in the digital age.
How blockchain can be used in the intellectual property (IP) ecosystem:
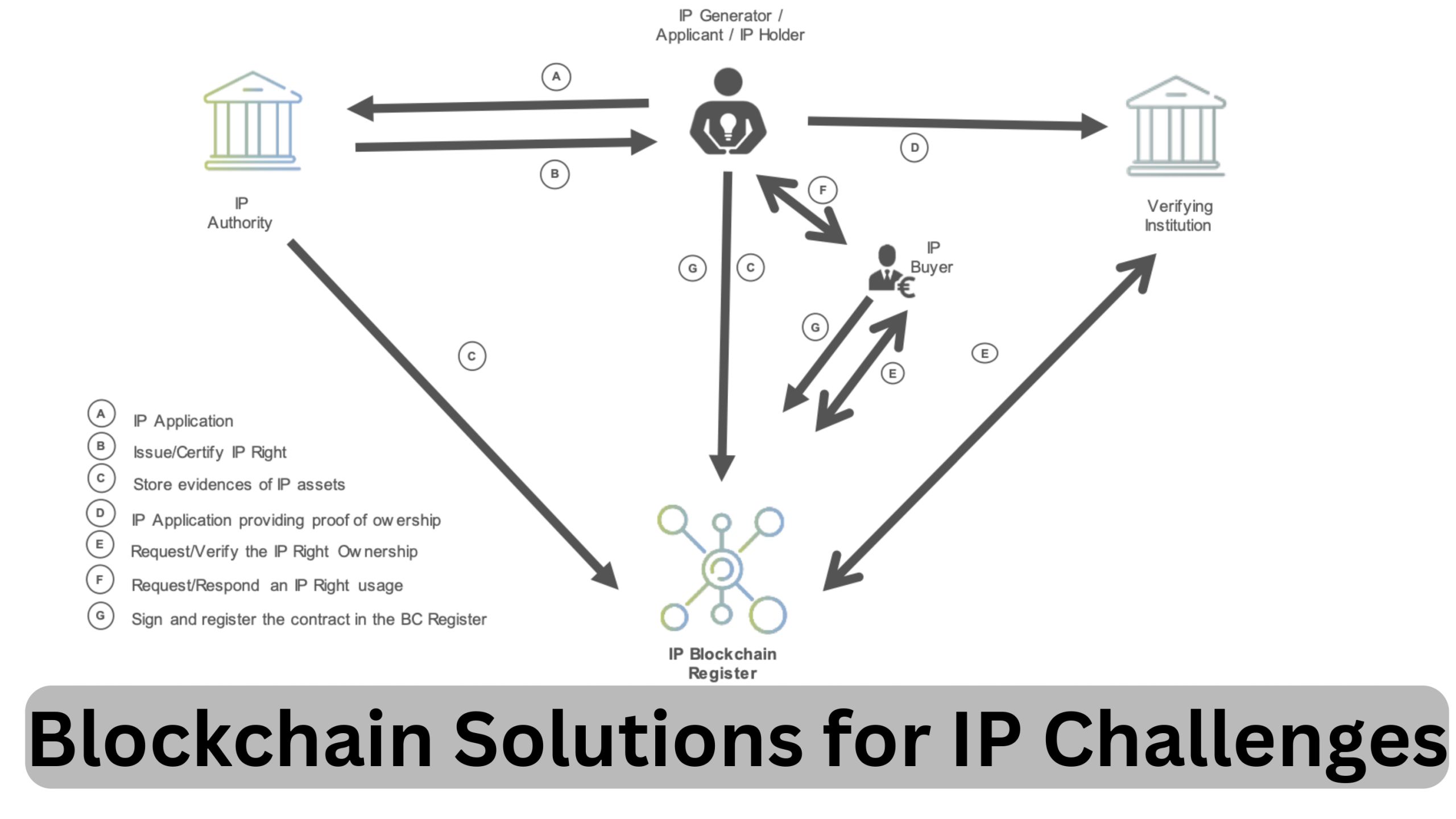
- IP Holder/Applicant Files with IP Authority:
The process begins with an IP holder or applicant filing for protection of their intellectual property rights with the relevant IP authority, such as the patent office, trademark office, or copyright office.
- Issue/Certify IP Right:
Once the IP application is received, the IP authority conducts examinations to determine if the application meets the criteria for intellectual property protection. If the application is successful, the IP authority issues and certifies the IP right, such as granting a patent, trademark registration, or copyright registration.
- Stores Evidence of IP Assets:
The IP Authority or IP Holder Can Store the evidence in the IP Blockchain Register. In a blockchain-based system, evidence of IP assets, such as patent documents, trademark certificates, or copyright registrations, can be stored securely on a blockchain register. Depending on the chosen blockchain infrastructure, this register can be maintained by either the IP authority or the IP holder themselves, depending on the chosen blockchain infrastructure.
- IP Applications Providing Proof of Ownership:
By storing IP assets on a blockchain, the IP holder can easily prove ownership of their intellectual property rights. The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that the ownership records cannot be altered or tampered with, providing robust proof of ownership.
- Request/Verify the IP Right Ownership:
The Verifying Authority Can Check with the Blockchain Register. When there is a need to verify the ownership of an IP right, the verifying authority, such as potential investors, licensees, or legal entities, can check the blockchain register. By accessing the blockchain register, they can confirm the authenticity and ownership status of the intellectual property assets.
- Request/Respond to an IP Right Usage:
The IP Holder Can Respond to the IP Buyer. For instance, in the case of licensing, selling, or assigning IP rights, the IP holder can interact directly with potential buyers or licensees. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can facilitate these transactions on the blockchain.
- Sign and Register the Contract in the Blockchain Register:
Once the agreement terms are finalized, the contract can be signed digitally by the involved parties. The signed contract, along with details of the transaction, can then be registered on the blockchain register. This registration provides a transparent and immutable record of the transaction, ensuring trust and security for all parties involved.
By leveraging blockchain technology in the intellectual property ecosystem, the process becomes more transparent, efficient, and secure, benefiting IP holders and stakeholders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the convergence of blockchain technology and intellectual property management represents a promising frontier in innovation. Companies like IPWe, IP Chain, Copytrack and IBM Blockchain are pioneering solutions that enhance IP rights management transparency, security, and efficiency in IP rights management. While blockchain holds immense potential to revolutionize the industry by addressing issues like authentication, verification, and piracy prevention, carefully considering its benefits and challenges is paramount. Although adopting blockchain in the IP ecosystem requires investment and collaboration, its impact on protecting and incentivizing innovation cannot be overstated. As the industry evolves, stakeholders must continue to study and assess the implications of blockchain technology to harness its full potential in safeguarding intellectual property rights.
*Written by Helan Benny, Legal Intern @Intepat IP